Why Permaculture Design Needs to be Adaptive
Permaculture design transcends mere farming techniques; it embodies a holistic approach to crafting sustainable ecosystems.
This exploration delves into the core principles of permaculture and highlights the critical need for adaptability in today s ever-evolving environment. Traditional design methods frequently falter in tackling the challenges at hand, which is why embracing adaptive strategies is vital for resilience and sustainability.
From essential elements of flexibility to illuminating real-life case studies, the practical insights offered here will undoubtedly inspire your own permaculture journey. Dive into the exciting world of adaptive permaculture design.
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Permaculture Design
- The Need for Adaptability in Permaculture Design
- Benefits of Adaptive Permaculture Design
- Key Elements of Adaptive Permaculture Design
- Implementing Adaptive Permaculture Design
- Case Studies of Successful Adaptive Permaculture Designs and Renewable Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is permaculture design and why does it need to be adaptive for climate adaptation?
- How does adaptability play a role in permaculture design?
- Why is it important for permaculture design to be able to adapt to changing conditions and climate change?
- What are some examples of situations where permaculture design needs to be adaptive?
- How does adaptive permaculture design benefit the environment?
- How Can Permaculture Design Be Made More Adaptive?
Key Takeaways:

- Adaptability is crucial in permaculture design to overcome challenges and limitations of traditional design approaches.
- Adaptive permaculture design leads to increased resilience and sustainability through flexibility, diversity, and integration of feedback and observation.
- Practical tips and case studies showcase the successful implementation of adaptive permaculture design in real-life situations.
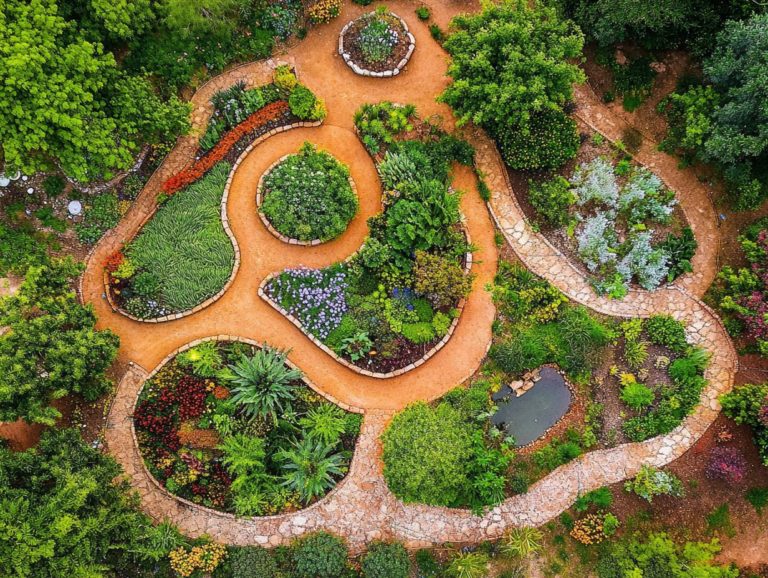
Understanding Permaculture Design
Understanding Permaculture Design is crucial as you embark on the journey to create sustainable agricultural systems that emphasize environmental sustainability and community resilience.
Founded by Bill Mollison, permaculture principles advocate for systems that can renew themselves, working in harmony with nature, supporting biodiversity (the variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat), and making efficient use of local resources.
This holistic approach nurtures ecological communities and promotes ethical land management practices that combat climate change and enhance food security.
Definition and Principles
Permaculture is a compelling design philosophy aimed at crafting systems that can renew themselves while enhancing biodiversity.
This innovative approach invites you to reexamine your relationship with the environment, fostering a profound understanding of the connection that binds all living systems. By prioritizing principles like Earth Care, which emphasizes the health of our planet, and People Care, which highlights the significance of community and well-being, you can develop sustainable practices that promote resilience in your surroundings.
Fair Share, another crucial tenet, advocates for the equitable distribution of resources, ensuring that the benefits derived from these systems are enjoyed by all. Through these guiding principles, permaculture addresses not just agricultural needs but also informs broader environmental planning, ultimately nurturing a more harmonious relationship between humanity and nature.
The Need for Adaptability in Permaculture Design
The necessity for adaptability in Permaculture Design has never been more critical, especially as climate change profoundly affects ecosystems and agricultural practices. This evolving landscape demands innovative strategies to foster resilience.
By acknowledging the constraints of traditional design methods, you can create flexible systems that flourish in diverse environmental conditions. This approach enhances soil health and cultivates a sense of community support, ensuring that your gardening practices remain robust and sustainable.
Challenges and Limitations of Traditional Design Approaches
Traditional design approaches in agriculture often struggle to tackle the complexities of climate impacts, which can undermine food security and sustainable practices.
These methodologies typically rely on monoculture systems and heavy chemical inputs, which degrade soil health and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. As climate change intensifies, the weaknesses of these systems become clearer, resulting in diminished crop yields and heightened pest outbreaks.
To respond effectively to broader climate challenges, it s crucial to explore innovative design frameworks that incorporate permaculture principles.
This strategy fosters biodiversity, enhances soil resilience, and promotes overall ecosystem health. By adopting this approach, you can pave the way for sustainable food production in an increasingly uncertain climate landscape.
Start your journey in adaptive permaculture today and watch your garden thrive!
Benefits of Adaptive Permaculture Design
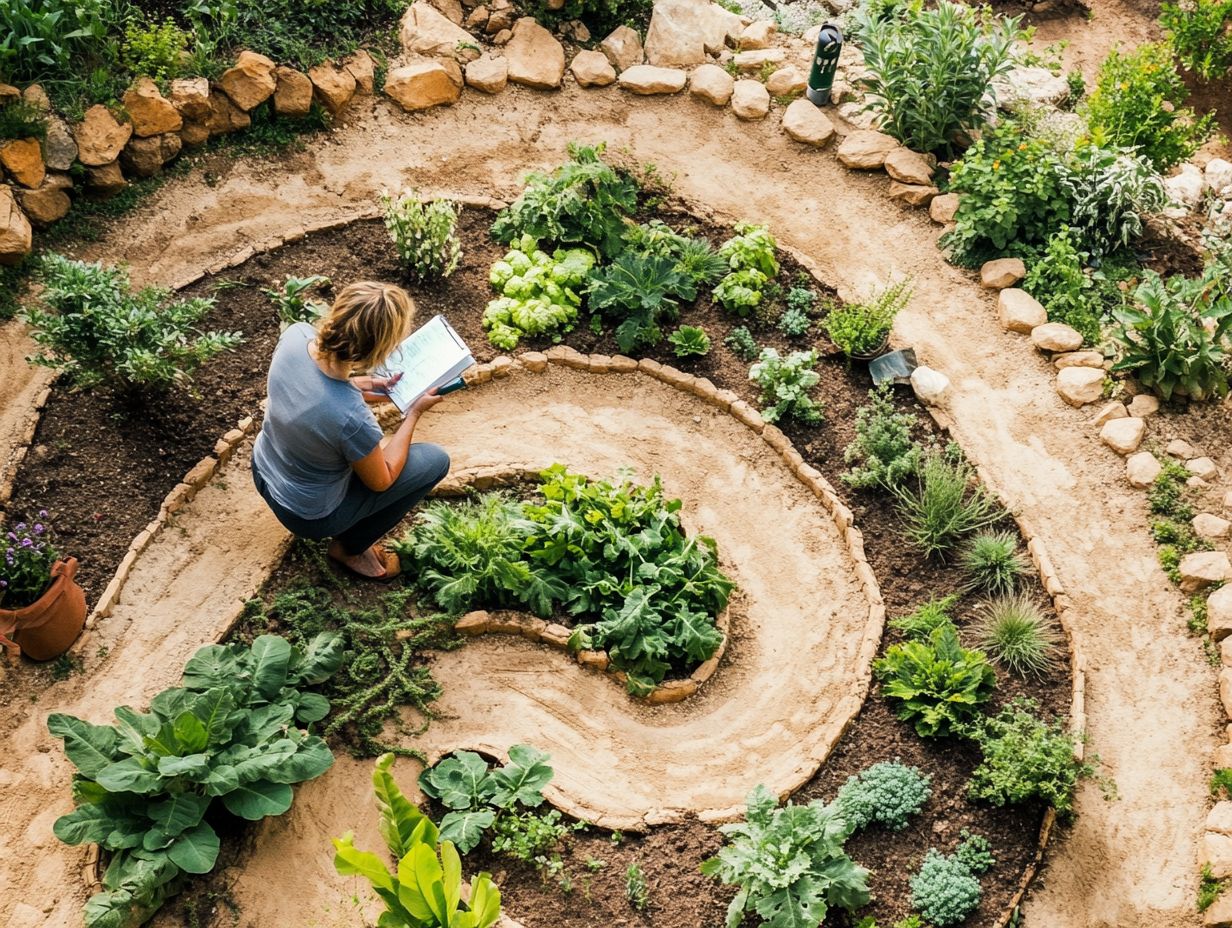

Engaging in adaptive permaculture design presents many advantages. It greatly improves the strength of farming systems while using renewable resources.
Increased Resilience and Sustainability
Increased resilience and sustainability are the main goals of adaptive permaculture systems. These systems can effectively respond to environmental challenges.
By following ecological principles, you boost the productivity of your land. This also enhances biodiversity and soil health, creating a balanced environment for plants and animals.
Community support is essential for this journey. Individuals come together to share resources, knowledge, and skills, strengthening local ecosystems.
This unity boosts your potential for innovation and adaptation. It helps you and your community tackle climate change and resource scarcity.
By merging shared efforts and ecological wisdom, you build a strong foundation for long-term sustainability.
Key Elements of Adaptive Permaculture Design
The key elements of adaptive permaculture design are flexibility and diversity. These aspects ensure that your design can adapt to environmental changes and your unique needs.
Flexibility and Diversity
Flexibility and diversity are vital in permaculture systems. They help create resilient ecological communities using techniques like companion planting.
By incorporating a variety of plants, animals, and microorganisms, you enhance resilience against pests and diseases. This fosters a web of symbiotic relationships.
Strategies like crop rotation and cover cropping maintain soil health and boost your yields. Embracing these principles allows life to flourish, leading to abundant harvests.
Integration of Feedback and Observation
Integrating feedback and observation techniques is critical in permaculture philosophy. This guides your design through action learning and adaptive strategies.
Create an interactive space for sharing insights with fellow practitioners. This allows for the continuous refinement of your designs.
Effective methods like regular assessments of plant health and soil conditions help adapt to the ever-changing dynamics of the ecosystem.
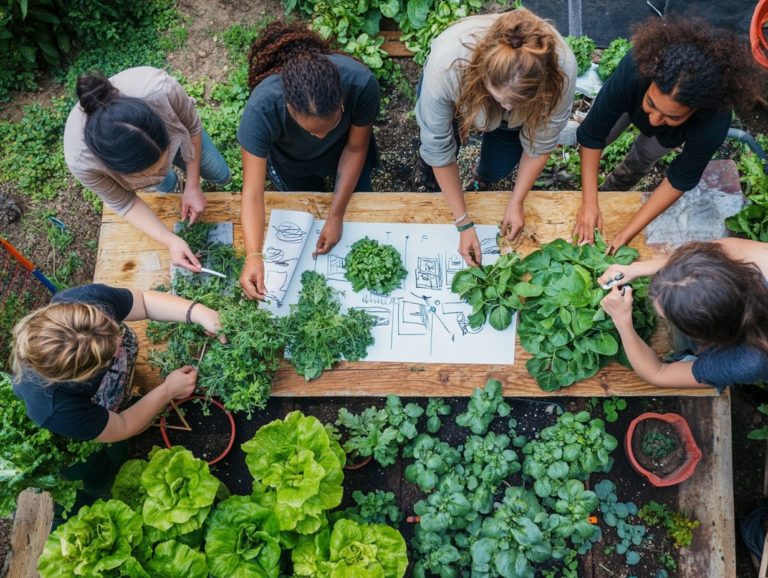
Community networks play a big role in this process. They provide platforms for collective learning and observation.
Implementing Adaptive Permaculture Design
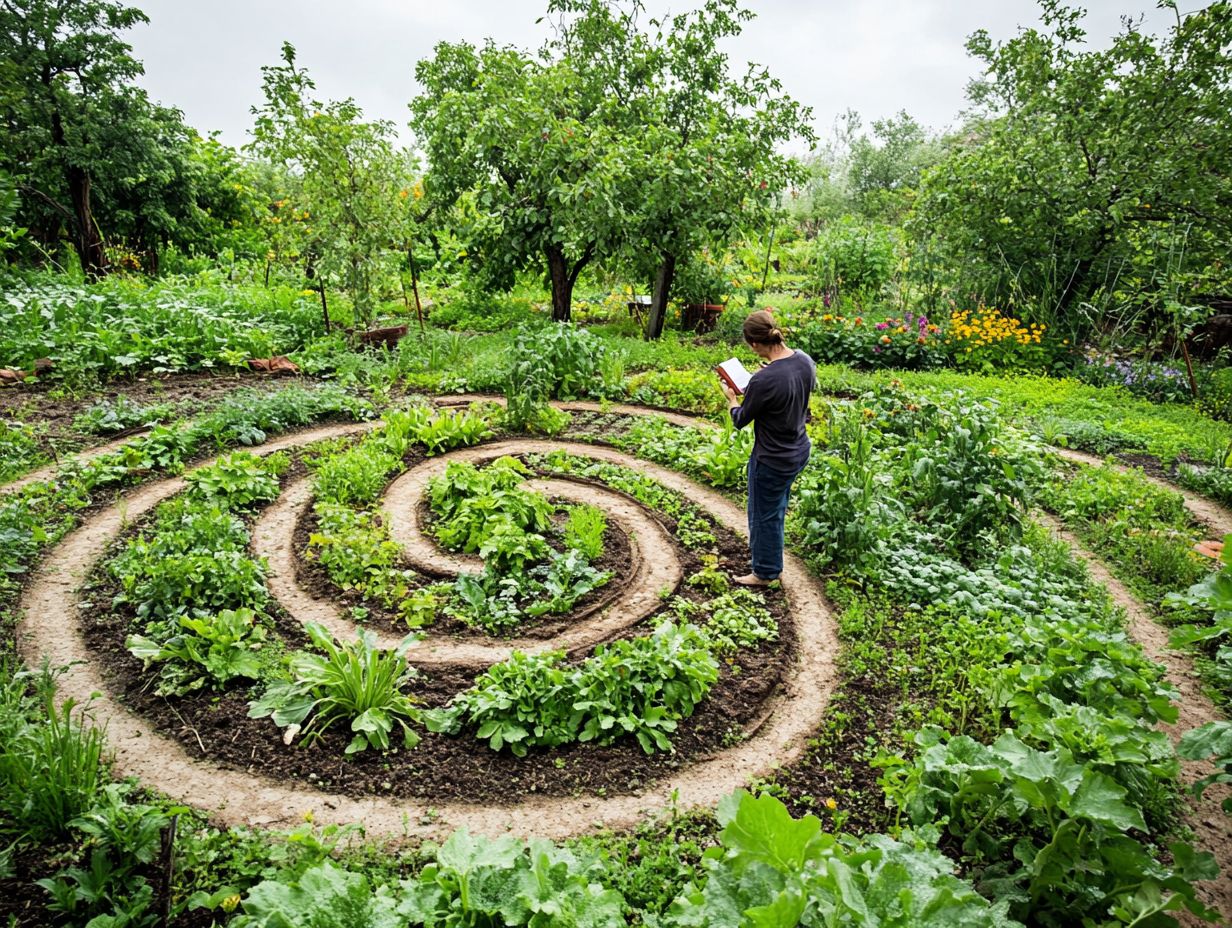

Implementing adaptive permaculture design involves practical tips and strategies. These not only enhance educational initiatives but also help communities adopt environmentally friendly practices.
Focus on these elements to cultivate a more resilient and sustainable ecosystem. Act now to harness these powerful techniques!
Practical Tips and Strategies
Embrace practical tips and strategies for success in adaptive permaculture design. Utilizing renewable resources and enhancing soil health are vital steps.
Equally important is managing water resources. Optimize this through techniques like rainwater harvesting and creating shallow ditches to direct runoff effectively.
Organic composting is another key player, allowing you to recycle kitchen and garden waste into nutrient-rich soil, promoting robust plant growth and biodiversity.
Building a strong network of community support amplifies these efforts. By sharing resources and knowledge with your neighbors, you not only bolster resilience but also cultivate a deeper sense of belonging.
These practices nurture thriving ecosystems and play a significant role in food security, ensuring that fresh produce remains available and accessible for everyone.
Case Studies of Successful Adaptive Permaculture Designs and Renewable Resources
Case studies of successful adaptive permaculture designs reveal innovative strategies that significantly enhance community resilience while promoting conservation initiatives.
By examining these examples, you can gain valuable insights into effective methods and observation techniques that foster sustainable living and strengthen communal bonds.
Real-life Examples of Adaptability in Action in Agri-Ecological Communities
Real-life examples of adaptability and climate impacts in action reveal how permaculture systems can respond to environmental challenges while nurturing biodiversity and building community networks and social equity.
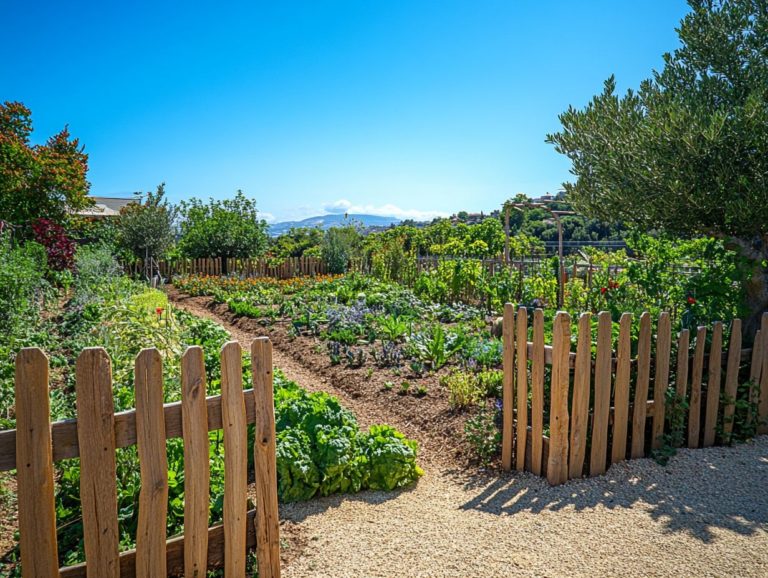
Consider a notable case study from a community in Australia that embraced permaculture principles to rejuvenate degraded land. By integrating a diverse array of plant species and employing contour gardening techniques, they restored soil health and cultivated a sustainable food source and water management for local residents.
Another inspiring example comes from a small farm in Vermont. Innovative practices like growing trees and crops together and renewable energy have bolstered resilience against climate variability.
These success stories showcase the amazing power of permaculture and how it transforms our ecological balance, illustrating how adaptive methodologies can enhance ecological balance and fortify community connections.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about permaculture design and its adaptability:
What is permaculture design and why does it need to be adaptive for climate adaptation?
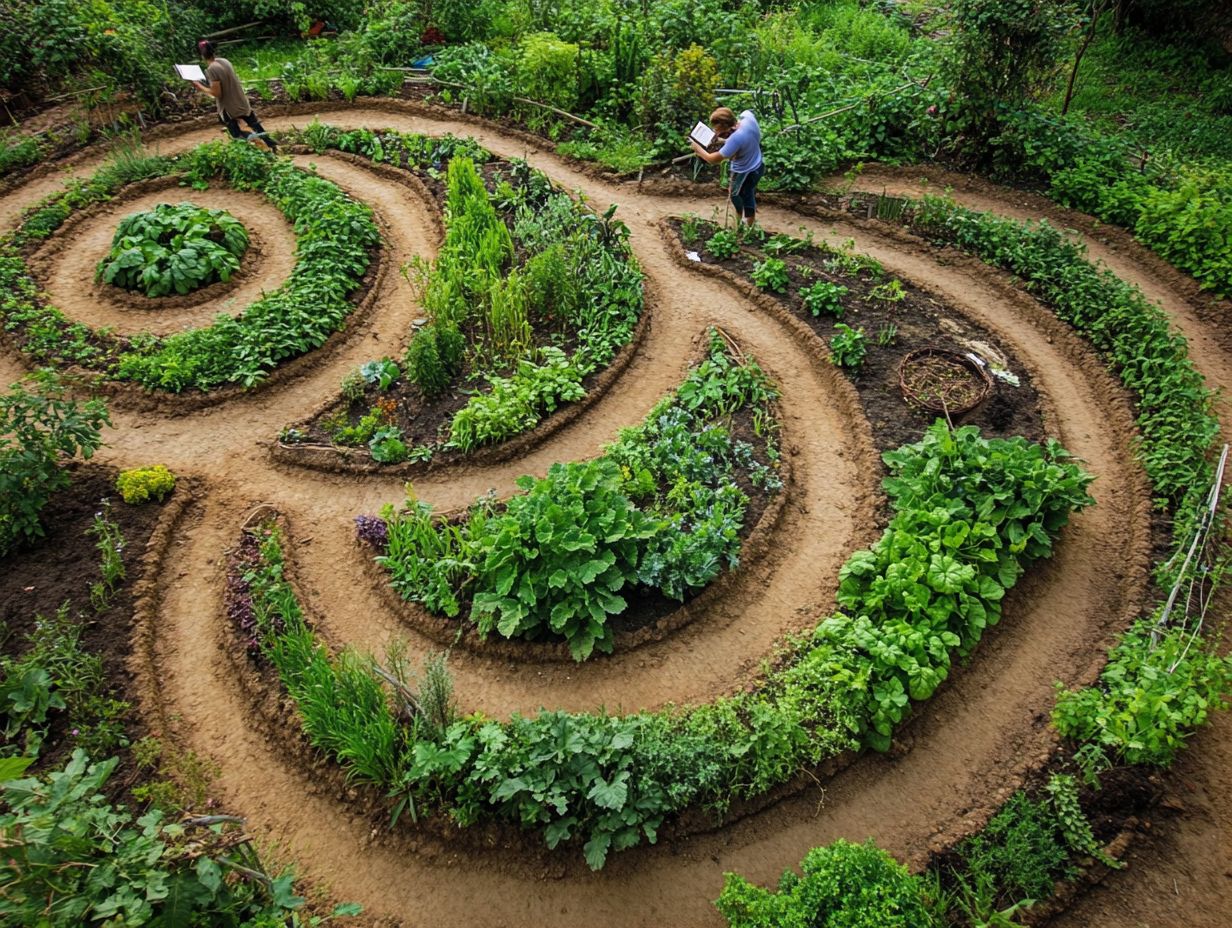

Permaculture design is an approach to sustainable living that incorporates regenerative systems and climate adaptation that mimics natural ecosystems to create an efficient and self-sustaining system. It needs to be adaptive because the environment and conditions are constantly changing, and a rigid design may not withstand these changes.
How does adaptability play a role in permaculture design?
Adaptability is a key element in permaculture design as it allows the system to adjust and respond to environmental changes, ensuring its sustainability and resilience.
Why is it important for permaculture design to be able to adapt to changing conditions and climate change?
Permaculture design aims to create long-term sustainable systems, and to achieve this, it must adapt to changing conditions. This allows the system to continue functioning and providing benefits even as the environment evolves.
What are some examples of situations where permaculture design needs to be adaptive?
Examples include changes in weather patterns, shifts in plant and animal populations, and variations in soil conditions and health. All of these factors can significantly impact the design and require adaptability to maintain success.
How does adaptive permaculture design benefit the environment?
By adapting to environmental changes, permaculture design can promote biodiversity, reduce waste, and conserve resources. It also helps build resilient systems that can withstand natural disasters and other challenges.
How Can Permaculture Design Be Made More Adaptive?
Designers can make their plans flexible and diverse. They can use local plants that thrive in the environment and regularly check the system for needed changes.
Involving the local community is crucial. Their insights can lead to designs that adapt better to real-life conditions.